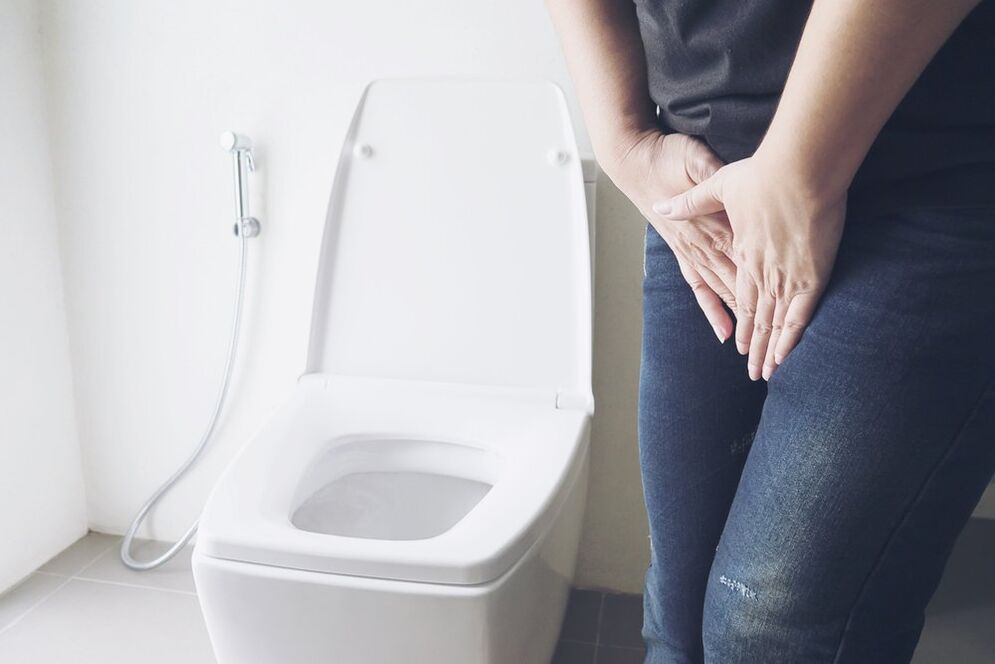
According to statistics, cystitis is more common in women than in men, which is related to the physiological differences in the structure of the urethra. The disorder is often accompanied by a series of unpleasant symptoms: pain and pain during urination, frequent urination, and lower abdominal pain.
Cystitis is a common disease of the urinary system. This is mainly due to the specificity of the anatomy, which is why cystitis is more common in women than in men.
What are the causes and first symptoms of cystitis in women? What are the main symptoms of cystitis in women? What types of cystitis are isolated? Which doctor treats cystitis and how can this disease be treated at home? Is it possible to prevent the development of cystitis and what needs to be done for this?
Cystitis in women: Is a doctor's appointment necessary?

Cystitis in women can be caused by various infectious diseases, worm invasion, bladder stones, the onset of menopause, endocrine system disturbances, and taking certain medications. In addition, there is interstitial cystitis, the exact mechanism of which has not been elucidated.
It should also be noted that cystitis in women can be acute or chronic. The chronic form is characterized by frequent relapses of the disease and slow, constant presentation of symptoms.
To prevent the disease from becoming a persistent source of discomfort, it is necessary to make an appointment with a doctor and receive the necessary treatment at the first signs of the disease. To do this, all you need to do is call the Archives Clinic. The experts who deal with this problem are urologists and gynecologists. Although, even a GP can treat the simpler form of the disease.
To diagnose cystitis in women, they usually do a urine test, a smear of the urethra and vagina. In chronic forms of the disease, testing for possible sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is also recommended.
Also, in some cases, additional tests are required, for which you must make an appointment with a nephrologist for an ultrasound or cystoscopy of the small pelvis.
The insidious thing about this disease is that treatment of cystitis is usually easy and the unpleasant symptoms go away quickly. As a result, many women prefer to self-medicate by purchasing advertised antimicrobials at pharmacies.
However, lack of proper treatment, short duration and wrong choice of drugs lead to the transformation of the disease into a chronic form, which in turn is difficult to treat. Therefore, you shouldn't take chances and use a friend's advice when choosing a medication - it's best to contact your doctor by phone and make an appointment. It should be remembered that prompt treatment not only avoids chronic cystitis, but also keeps other organs from spreading the infection.
Which symptoms of cystitis are most likely to cause discomfort?
Symptoms of acute cystitis in women always appear suddenly. These include:
- frequent and strong urge to urinate;
- Increased white blood cell content in the urine and a change in odor;
- blood in the urine;
- pain in the lower abdomen after cutting;
- burning and pain when urinating;
- Elevated body temperature.
These symptoms develop very quickly. About every quarter of an hour, women have to go to the toilet, and each time they go to the toilet, the amount of urine is very small. Additionally, bladder muscle spasms can lead to incontinence.
Cystitis tends to recur. Most women seek help at least once a year.
In the chronic form of the disease, symptoms are less pronounced. For example, the discomfort when urinating appears rather mild. The frequency of going to the toilet also did not change. Generally speaking, a person can live a normal life and participate in work (study).
Methods of preventing and treating cystitis

To understand possible ways to prevent and treat cystitis in fairer sex, it is necessary to identify the main cause of the disease. These include:
- Structural features of the female urethra (shorter and wider than males);
- hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, menopause), which disrupt the balance of the microflora and weaken the strength of local immunity;
- Urinary tract infections (may occur due to inadequate personal hygiene, unprotected intercourse);
- Trauma (eg, when using a catheter to transfer urine).
Cystitis can also occur as a concomitant disease of diabetes or urolithiasis. By the way, it is impossible to "earn" the disease with hypothermia. Similar symptoms suggest the development of polyuria (cold diuresis).
Therefore, in the face of cystitis, the first thing to do is to call the clinic and make an appointment with the doctor. Only experienced specialists determine the presence of an inflammatory process based on tests and prescribe the correct antibiotic treatment. It relieves most of the unpleasant symptoms for the first few days.
In addition, treatment of cystitis includes taking pain relievers and antipyretics. Doctors recommend observing an adequate drinking regimen during treatment, which will speed recovery (bacteria will be flushed out of the body faster through urine).
Experts have gone out of their way to warn that treating the disease on its own is dangerous. In fact, many genitourinary diseases have symptoms similar to bacterial cystitis and cannot be cured with a single antimicrobial drug. As a result, you can waste valuable time and face serious health threats.
Measures to prevent this disease are:
- Personal hygiene (changing underwear daily, changing pads frequently, and showering regularly);
- Wear selected underwear made of natural materials;
- Prompt treatment of all existing urogenital disorders;
- Toilets and showers must be used after sex.
If a flare-up occurs while on the road or on vacation, you should try to avoid hypothermia, drink plenty of fluids, limit spicy and salty foods, and drink alcohol until you seek medical help.
If you have chronic cystitis, before a long trip, you should see your doctor and discuss with him a set of medications that you should take with you on your trip. And (if possible) use his phone number for emergency communications.